General
A contactor is a switching device, widely used for the switching of motors, capacitors (for power factor correction), and lights. As the name indicates it is used to make or break contacts like an ordinary on-off switch. The only difference is that the contactors have an electromagnet that holds the contacts when energized whereas switches do not have it.
Their basic principle of operation is the same as that of electromechanical relays, the difference being, contactors are designed to can carry much more current than relays. Relays cannot be directly used in circuits where the current exceeds 20 amperes. Whereas contactors are available in a wide range of ratings and forms. Also, they are available up to the ampere rating of 12500A. They cannot provide short-circuit protection but can only make or break contacts when excited.
What is the working principle of AC contactor?
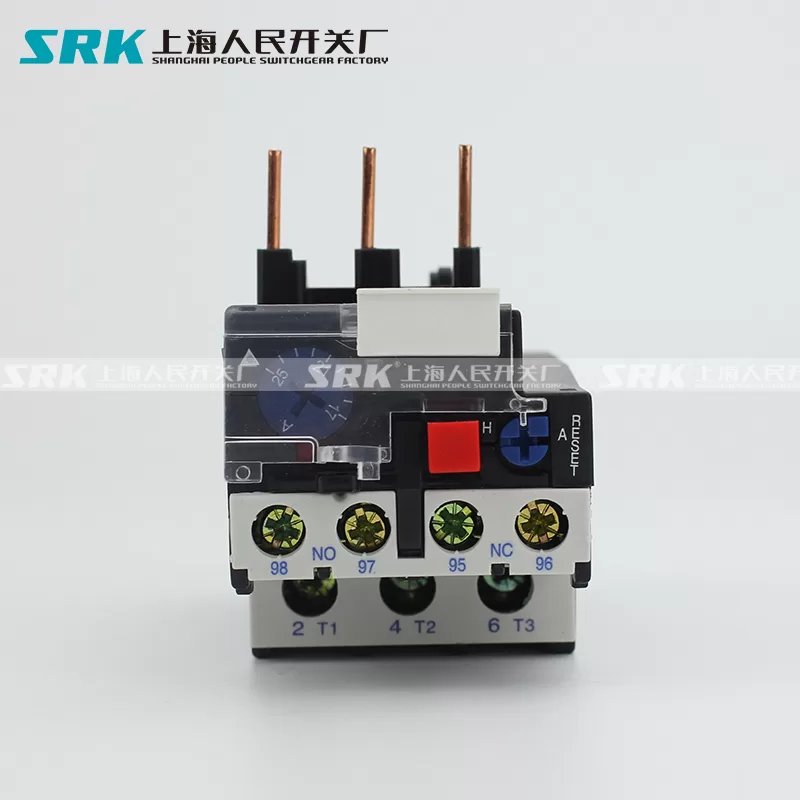
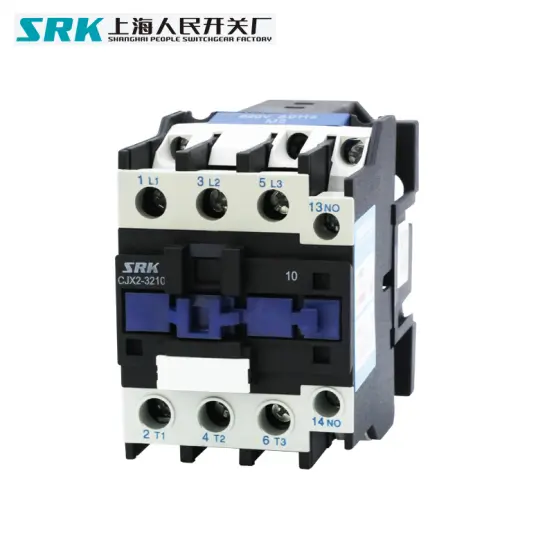
The AC contactor is an electromagnetic AC contactor with a NO main contact, three poles, and air as the arc extinguishing medium. Its components include: coil, short-circuit ring, static iron core, moving iron core, moving contact, static contact, auxiliary NO contact, auxiliary NC contact, pressure spring sheet, reaction spring, buffer spring, arc extinguishing The cover is composed of original parts. The appearance structure of the common AC contactor is shown in the figure below:
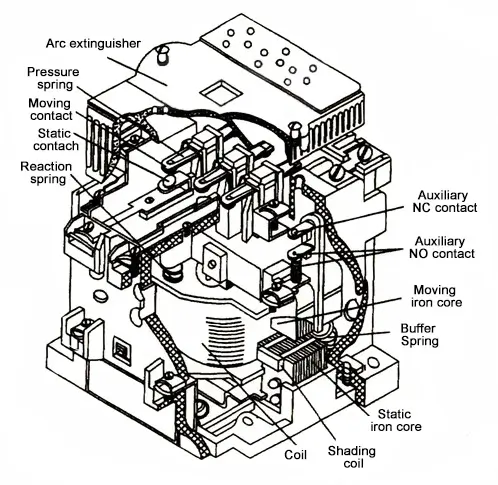
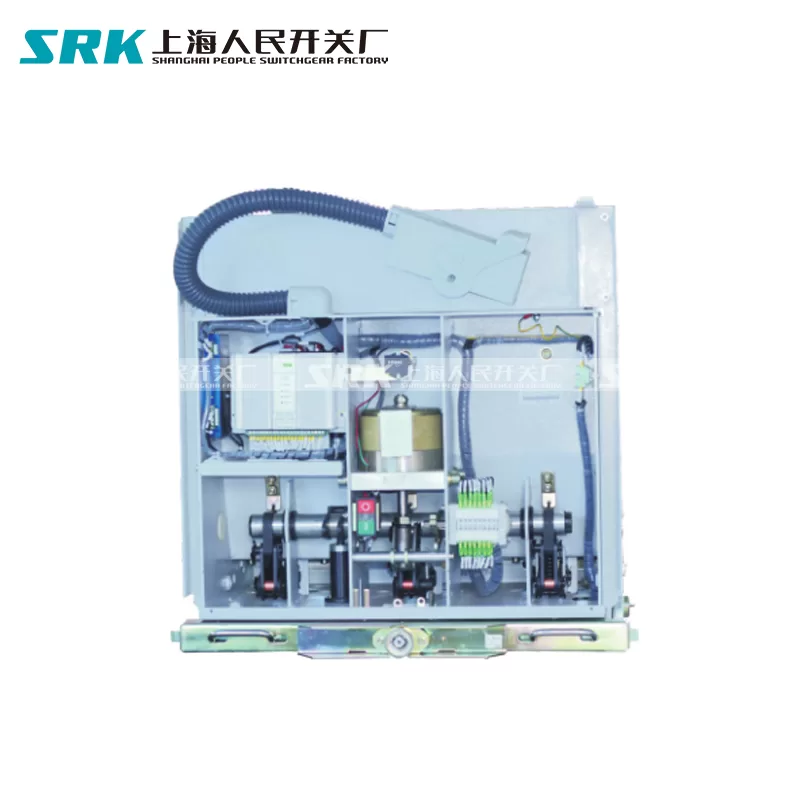
Electromagnetic system: It includes coil, static iron core and moving iron core (also called armature).
Contact system: It includes main contacts and auxiliary contacts. The main contact allows a larger current to pass through and plays the role of connecting and cutting off the main circuit. Usually, the maximum current allowed by the main contact (ie, the rated current) is one of the technical parameters of the contactor. Auxiliary contacts are only allowed to pass small currents, and are generally connected to the control circuit when used.
The main contacts of AC contactors are generally NO contacts, and the auxiliary contacts are either NO or NC. A contactor with a smaller rated current has four auxiliary contacts; a contactor with a larger rated current has six auxiliary contacts.
NO and NC refer to the state of the contacts before the electromagnetic system is energized. That is, the NO contact means that when the coil is not energized, its moving and static contacts are in an open state, and the coil is closed after it is energized. NC contact means that when the coil is not energized, its moving and static contacts are closed, and when the coil is energized, it is disconnected.
The function of the arc extinguishing device is to quickly cut off the arc when the main contact is broken. If it is not cut off quickly, the main contact singeing and welding will occur. Therefore, AC contactors generally have arc extinguishing devices. For AC contactors with larger capacity, arc extinguishing grids are often used.
The working principle structure of the AC contactor is shown in the figure below. When the coil is energized, the iron core is magnetized, attracting the armature to move downward, making the normally closed contact open and the normally open contact closed. When the coil is de-energized, the magnetic force disappears. Under the action of the reaction spring, the armature returns to the original position and the contact returns to the original state.
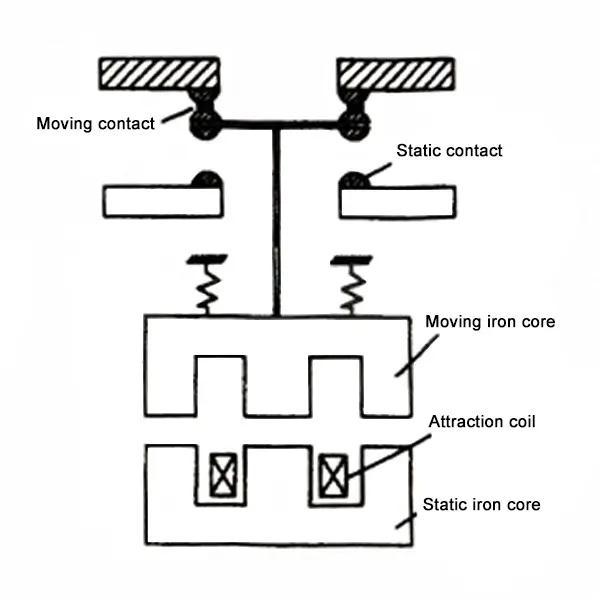
How Does a Contactor Device Work?
To understand the contactor working, you need to know the various parts of a contactor. There are three essential components of a contactor;
The coil/electromagnet
Contacts
The frame or enclosure
Coil or electromagnet
The coil provides the driving force in a contactor that closes the contacts. It features a coil wound around an electromagnetic core and thus behaves like an electromagnet. The coil has two parts, a fixed one and a movable part with a spring connecting both parts. This structure creates a spring return mechanism.
A rod called an armature is connected to the movable part. When the coil’s force is more than the spring’s force, both contacts connect. When the spring’s force is more than the coil’s force, the contacts disconnect.
The input of the contactor coil could either be AC or DC. This current comes from an external control circuit for the contactor and serves to excite the electromagnetic core. For AC contactors, soft laminated iron is the electromagnetic core material. It helps reduce the eddy current loss. In DC contactors, solid steel is the material for the electromagnetic core as the issue of eddy current does not arise.
Contacts
Contacts perform the current carrying function in a contactor. There are different types of contacts in a contactor, and they are; auxiliary contact, power contact, and contact spring. The power contact has two types that are; stationary and movable contact.
Material for making contacts must have a high welding resistance and stable arc resistance. The material should also withstand erosion and mechanical stress. In high current and DC applications, the material is silver tin oxide, while in low current applications, the material is silver nickel and silver cadmium oxide.
Enclosure
As the name suggests, the enclosure protects the internal parts of the contactor. It shields the contacts from dust, bad weather, explosion hazards, and oil. It also prevents personnel from touching the contacts.
The contactor working, in a nutshell, is as follows
Current from the external control circuit passes through the contactor, exciting the electromagnetic core. In turn, the coil/electromagnet creates a magnetic field which makes the contactor move the armature. A normally closed contact then makes the circuit complete between the fixed and moving contacts. The current is then able to pass through these contacts to the load.
When the current is removed, the coil becomes de-energized, and the magnetic force falls to zero. The spring force is thus higher and pulls back the armature opening the circuit. The design of contactors facilitates rapid ON-OFF action.


Contact us:
Kani Xie
SHANGHAI PEOPLE SWITCHGEAR FACTORY
E-mail:Kani@srkswitchgear.com
Ph: 0086 13695872200
Wechat/ WhatsApp/skype: +86 13695872200























